Cryptocurrency has become more than just a trend—it is shaping the future of finance. As digital coins like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other altcoins grow in popularity, understanding how to store and manage them safely is crucial. This is where a crypto wallet comes in.
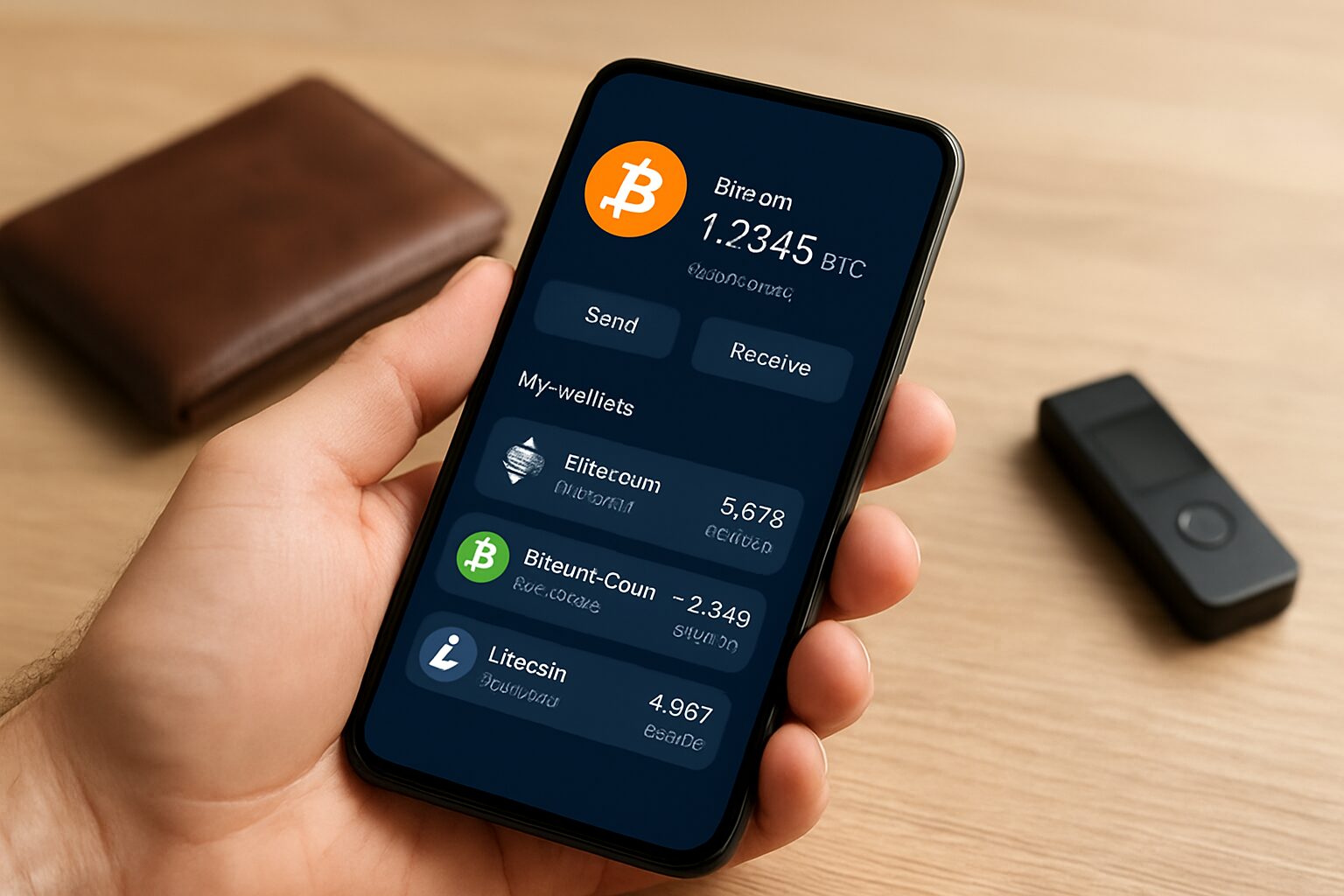
A crypto wallet is a digital tool that allows you to store, send, and receive cryptocurrencies securely. Unlike a traditional wallet or bank account, it does not hold physical money but provides access to your digital assets on the blockchain. For beginners and investors, understanding crypto wallets is essential for safeguarding investments and navigating the crypto world confidently.
What Is a Crypto Wallet?
A crypto wallet is software or hardware that stores private and public keys, enabling you to interact with the blockchain. While it might seem similar to a traditional wallet, it is different in that it does not physically store coins. Instead, it grants access to your cryptocurrency holdings.
Why are crypto wallets important?
Crypto wallets are important because they keep your digital assets safe and under your control. They keep your private keys safe. These keys show that you own your cryptocurrency and let you send, receive, and handle your money without using an exchange. Wallets also keep your coins safe from threats like exchange hacks, freezes, or shutdowns. They also make long-term storage safer, protect your privacy better, and give you access to decentralized apps, staking, and other blockchain services.
How do you use a crypto wallet?
First, decide what kind of crypto wallet you want to use. You can choose a mobile, desktop, hardware, or web wallet. Then, set it up by making a new wallet and making sure you have a safe copy of the recovery phrase. Once everything is set up, you can share your wallet address or QR code to receive crypto, and you can enter the address, amount, and network of the person you want to give crypto to. Before completing a transaction, you should always check the address and make sure it works with the network. Your wallet can also be used to keep an eye on your funds, connect to decentralized apps, stake assets, or trade tokens. Your private keys and recovery phrase will always be safe.
Key Functions:
- Sending and Receiving Coins: Wallets allow you to transfer crypto to others safely.
- Storing Coins: Wallets keep your assets secure by protecting private keys.
- Security: Private keys are like passwords; anyone with access can control your funds.
In short, a crypto wallet is your personal gateway to securely using cryptocurrencies.
How a Crypto Wallet Works
Crypto wallets operate using complex blockchain technology but can be simplified for everyday use.
Public Key vs Private Key
- Public Key: Like your bank account number, it is safe to share and allows others to send crypto to you.
- Private Key: Similar to your PIN, it must be kept secret as it grants access to your funds.
Transaction Process
When you send crypto, your wallet creates a transaction, signs it with your private key, and broadcasts it to the blockchain. Once verified, the transaction is recorded permanently.
Hot Wallets vs Cold Wallets
- Hot Wallets: Online wallets that are connected to the internet; convenient but more vulnerable to hacks.
- Cold Wallets: Offline wallets that are safer but less accessible.
Common Features
- Balance tracking
- Transaction history
- Integration with exchanges for trading
Types of Crypto Wallets
Hot Wallets (Online Wallets)
- Web Wallets: Accessed via browser; convenient but prone to phishing attacks.
- Mobile Wallets: Apps for smartphones; good for daily transactions.
- Desktop Wallets: Installed on a computer; safer than web wallets but can be hacked if the device is compromised.
Pros: Easy access, user-friendly Cons: Higher risk of hacks
Cold Wallets (Offline Wallets)
- Hardware Wallets: Devices like Ledger and Trezor; store keys offline.
- Paper Wallets: Printed private and public keys; fully offline.
Pros: Highly secure Cons: Less convenient for frequent transactions
Custodial vs Non-Custodial Wallets
- Custodial Wallets: Third party controls your private keys (e.g., exchanges)
- Non-Custodial Wallets: You control the keys; more responsibility but greater security
Examples of Popular Crypto Wallets
- Software Wallets: MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Coinbase Wallet
- Hardware Wallets: Ledger, Trezor
Comparison Table:
| Wallet | Type | Security | Usability | Supported Coins |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MetaMask | Software | Medium | High | Ethereum & ERC-20 |
| Trust Wallet | Software | Medium | High | Multi-chain |
| Coinbase Wallet | Software | Medium | High | Multi-chain |
| Ledger | Hardware | High | Medium | Multi-chain |
| Trezor | Hardware | High | Medium | Multi-chain |
How to keep your cryptocurrency wallet secure
Protect your private keys and password phrase first to keep your cryptocurrency wallet safe. Keep them somewhere offline, don’t share them, and don’t save them as plain text on your phone or computer. When you can, use strong, unique passwords and two-factor security. Pick wallets that you can trust, make sure your software and devices are up to date, and watch out for phishing links, fake apps, and messages you didn’t ask for. If you have a lot of coins, you might want to use a hardware wallet. Just make sure you connect it only to safe devices and networks to keep your coins safe.
How to Choose the Right Crypto Wallet
Factors to Consider
- Security: Hardware wallets are best for long-term storage.
- Usability: Mobile wallets are convenient for daily use.
- Supported Cryptocurrencies: Ensure your wallet supports the coins you own.
- Cost: Some wallets are free, others may have a purchase price.
Tips for Safety
- Backup your wallet regularly
- Enable multi-factor authentication
- Avoid public Wi-Fi when accessing wallets
- Keep private keys private
Common Mistakes to Avoid
A common mistake people make when working with crypto wallets and exchanges is leaving large amounts of cryptocurrency on platforms instead of moving them to a safe wallet. Too many users also don’t back up their recovery words properly or store them online, which leaves them open to being stolen or lost. If you send money without checking to see if the network is compatible, you could lose the money forever. If you fall for phishing scams or fake apps, your credentials are often taken. Lastly, even the best crypto tactics can be easily hacked if you don’t follow basic security rules. For example, using weak passwords, old software, and not managing your risks can all be very bad.
Conclusion
A crypto wallet is an essential tool for anyone involved in cryptocurrency. Understanding how it works, the types available, and best practices for security can protect your digital assets and give you peace of mind. Choose the wallet that fits your needs and start managing your crypto safely today.
FAQs
1. What is the safest type of crypto wallet?
Hardware wallets (like Ledger or Trezor) are considered the safest because they store private keys offline, reducing the risk of hacking.
2. Can I recover my crypto wallet if I lose access?
Yes, if you have your backup seed phrase or recovery keys. Without it, access to your crypto is permanently lost.
3. How much does a crypto wallet cost?
- Software wallets: Usually free.
- Hardware wallets: Typically $50–$250, depending on brand and features.
4. Are crypto wallets insured?
Most crypto wallets are not insured. Some custodial wallets on exchanges may offer limited insurance, but self-custodied wallets are generally your responsibility.
5. What is the difference between hot and cold wallets?
- Hot wallets: Online, convenient for trading, but more vulnerable to hacks.
- Cold wallets: Offline, highly secure, but less convenient for frequent use.
6. Can I use the same wallet for multiple cryptocurrencies?
Yes, many wallets support multiple coins, but some are coin-specific. Always check supported cryptocurrencies before use.
7. How do I back up my crypto wallet?
- Write down your seed phrase securely.
- Store backups offline in a safe place.
- Avoid digital copies on phones or cloud storage that could be hacked.
8. Are mobile wallets safe?
Mobile wallets are convenient and generally safe if you:
- Use official apps
- Keep your phone updated
- Avoid public Wi-Fi when transacting
9. What happens if I forget my private key?
If you lose your private key and don’t have a backup, you lose access to your funds permanently. There’s no way to recover it without the key.
10. Can exchanges be trusted to hold my crypto?
Some major exchanges are secure, but storing large amounts there carries risk. For long-term storage, a non-custodial wallet is safer.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial or investment advice. Cryptocurrency investments carry risk, and you should do your own research before making any decisions.