Cryptocurrency, or crypto, is digital money that only exists online. It’s decentralized, meaning no bank or government controls it.
- History in a nutshell:
- 2009: Bitcoin (BTC) launched by “Satoshi Nakamoto.”
- 2015: Ethereum (ETH) introduced smart contracts.
- 2024–25: ETFs gain approval, institutional interest surges.
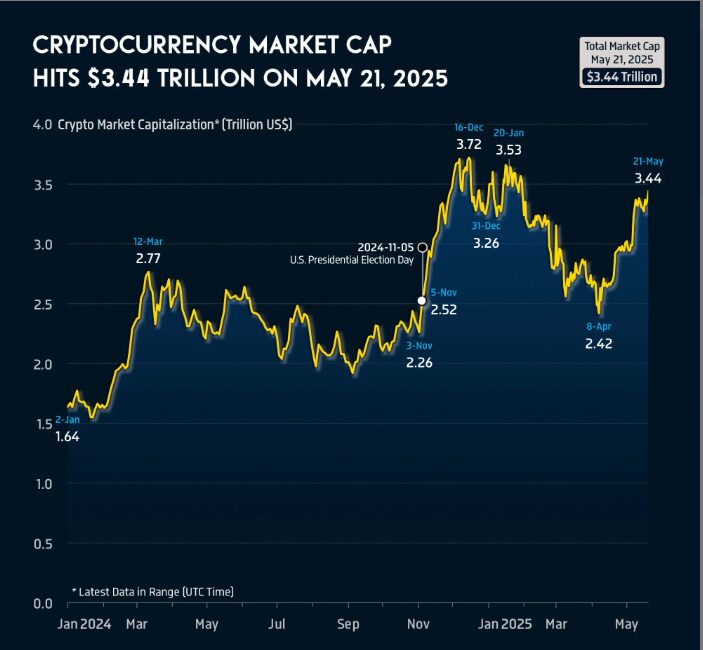
Why it matters in 2025: Today’s total crypto market sits at $3.4 trillion up around 40% year-over-year. With Bitcoin ETFs approved and even the U.S. government exploring digital asset reserves, this space is booming.
What is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a kind of digital money that uses cryptography for security and works on decentralized networks known as blockchains. Unlike regular money from governments, cryptocurrencies are not managed by any central authority. This makes transactions clear, safe, and often quicker across countries. They can be used for payments, investments, or to hold value, and their prices change based on market demand, how widely they are accepted, and other economic factors. Common examples include Bitcoin, Ethereum, and different altcoins.
How Does Cryptocurrency Work?
Cryptocurrency operates using blockchain technology, which is a digital record that is not controlled by any single entity and keeps track of all transactions over a network of computers. Each transaction is checked by people known as miners or validators, which helps keep things safe and stops fraud or spending the same money twice. Once confirmed, transactions are combined into blocks and added to the chain, making a lasting and clear record. Users keep their cryptocurrency in digital wallets that use private keys to access and approve transactions. This system lets cryptocurrencies work without central banks or middlemen, allowing people to send money directly to each other anywhere in the world.
Types of Cryptocurrency
A. Bitcoin (BTC) – The Original Crypto
- Unique features:
- First crypto ever.
- Limited to 21 million coins—called “digital gold.”
- Serves as a store of value and inflation hedge.
- Store of value: People hold it for long-term savings, similar to gold.
B. Altcoins – Alternatives to Bitcoin
- Ethereum (ETH):
- Introduced smart contracts and dApps—software that runs on blockchain.
- Other altcoins: Litecoin, Ripple (XRP), Cardano (ADA), Solana (SOL), and more—each with unique tech or niche.
C. Stablecoins
- Pegged to real currencies (e.g., USD). Examples: USDT, USDC.
- Use case:
- Keeps value steady.
- Great for trading, remittances, and everyday use.
D. Meme Coins
- Examples: Dogecoin, Shiba Inu.
- Based on internet culture—often volatile and speculative.
E. Utility Tokens & Security Tokens
- Utility tokens: Grant access to a service (e.g., BNB, UNI).
- Security tokens: Represent ownership in real assets (like stocks or real estate).
F. CBDCs (Central Bank Digital Currencies)
- Government-backed digital money:
- Issued by central banks.
- Different from decentralized crypto because they are government-controlled.
How to Use Cryptocurrency
- Sending/Receiving:
- Share your wallet address to receive funds.
- Paying:
- Some shops and online services accept crypto payments.
- Investing & Trading:
- Buy low, sell high—be mindful of market swings.
- DeFi & NFTs:
- Join decentralized finance (DeFi) to lend, borrow, or earn interest.
- Trade NFTs—digital ownership of art or collectibles.
Pros and Cons of Crypto
| ✅ Pros | ⚠️ Cons |
|---|---|
| Decentralization & freedom | High price volatility |
| Low fees and global reach | Regulations change rapidly |
| Secure and clear records | Risk of scams or hacks |
How to buy cryptocurrency
Buying cryptocurrency in 2025 is easier than ever, and you can get started in just a few simple steps. First, choose a reliable crypto exchange like Binance, Coinbase, Kraken, or a local platform such as Coins.ph if you’re in the Philippines. These exchanges allow you to trade your local currency (like PHP or USD) for digital assets.
Once you’ve picked an exchange, you’ll need to sign up and verify your identity by submitting documents such as a government-issued ID and proof of address—this is part of a standard process called KYC (Know Your Customer) to ensure your account is secure. After your account is verified, the next step is to deposit funds. Most exchanges accept various payment methods, including bank transfers, credit or debit cards, and popular e-wallets like GCash or PayPal. With funds in your account, you can now choose which cryptocurrency you want to buy.
For beginners, Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH) are usually good starting points due to their popularity and long-term growth. Other beginner-friendly coins include Solana (SOL), Binance Coin (BNB), and stablecoins like USDT or USDC, which are pegged to the value of the US dollar. When you’re ready to make a purchase, simply go to the “Buy” or “Trade” section of your chosen exchange, select your desired crypto, enter the amount you want to buy, and confirm the transaction. Congratulations—you now own cryptocurrency!
What can you buy with cryptocurrency?
You can buy a surprising number of things with cryptocurrency today, as more businesses and platforms accept it as a form of payment. The most commonly accepted cryptos are Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and stablecoins like USDT or USDC.
You can use cryptocurrency to buy everything from electronics, travel tickets, and fashion to NFTs, subscriptions, and even groceries in some places. As adoption grows, your crypto wallet is becoming more like a real-world spending tool—but with more flexibility and global reach.
Is Crypto Safe and Legal?
Cryptocurrency is usually legal in many countries, but the level of safety and rules about it can be very different. It can be safe if you take the right steps, like using trusted wallets, exchanges, and good security habits. However, crypto also faces risks such as hacking, scams, and changes in the market. Leyes sobre criptomonedas varían según el país: algunos las aceptan por completo, otros ponen limitaciones y algunos las prohíben totalmente. Investors need to know the laws and security steps that are necessary before using or investing in cryptocurrency.
Future of Cryptocurrency
- Emerging trends:
- Web3: A user-controlled internet.
- AI + crypto: Smart trading tools and automation.
- Crypto gaming: Play-to-earn economies.
- Institutional adoption: Loans secured by crypto, government reserves, ETFs.
- Fiat vs Crypto?: Likely a dual-money system—crypto complements fiat, but probably won’t replace it entirely.
Crypto Market Snapshot (Mid‑2025)
- Total market cap: $3.4 trillion (up ~40% YoY).
- Bitcoin share: 63–64% of total trading volume.
- BTC market cap: $2.11 trillion, up ~77% YoY.
- 2025 target: analysts estimate total may reach $8 trillion by late 2025.
Cryptocurrency fraud and cryptocurrency scams
Cryptocurrency fraud and scams have become increasingly common as the popularity of digital assets grows. Because crypto transactions are often irreversible and pseudonymous, scammers take advantage of beginners or careless investors.
Cryptocurrency fraud involves any dishonest scheme designed to steal your crypto assets or trick you into giving them away. It often involves fake investments, impersonation, or phishing attacks—and it can happen to anyone, from first-time buyers to seasoned traders.
1. Phishing Scams
You receive fake emails, text messages, or websites that look like a real crypto exchange or wallet provider. These messages try to trick you into entering your private keys, login credentials, or seed phrase.
💡 Tip: Always check the URL, and never enter your private information unless you’re 100% sure it’s legit.
2. Fake Crypto Exchanges or Wallets
Some scammers create entire fake platforms that look like popular exchanges. You deposit your funds, and then—poof!—your money is gone, and so is the site.
💡 Tip: Use only well-known and trusted exchanges like Binance, Coinbase, or Kraken.
3. Pump and Dump Schemes
In these scams, a group hypes up a low-value coin (often via social media), causing prices to soar. Once enough people buy in, the original promoters sell everything, causing the price to crash and leaving others with worthless tokens.
💡 Tip: Be cautious of coins that are suddenly trending and being hyped without real utility.
4. Giveaway Scams
These are often found on X (formerly Twitter), YouTube, or Telegram. Scammers impersonate celebrities or crypto influencers and offer “free crypto” if you first send them a small amount.
💡 Warning: No one will ever ask you to send crypto to receive more in return. If it sounds too good to be true—it is.
5. Impersonation Scams
Scammers pose as customer support, friends, or even government agents asking for your wallet details or access to your account. They may call, email, or DM you.
💡 Tip: Legitimate companies will never ask for your password or private key.
6. Rug Pulls
These happen when a new project (usually DeFi or NFT-related) promises big returns. People invest, and once the creators collect enough funds, they disappear—along with your money.
Tip: Research any project thoroughly. Look for transparent teams, audits, and community trust.
7. Ponzi or Pyramid Schemes
These scams rely on recruiting others to invest so early investors get paid. They often use terms like “guaranteed daily ROI” or “passive crypto income.”
Tip: If a project depends more on referrals than a real product, it’s likely a scam.
Crypto Scam Statistics (2024–2025)
| Type of Scam | % of Total Losses | Estimated Loss (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Investment scams | 50%+ | $4.6 billion+ |
| Romance scams | 15% | $1.2 billion |
| Phishing scams | 10% | $900 million |
| Rug pulls | 20% | $2.1 billion |
(Source: Chainalysis Crypto Crime Report 2025)
How to Protect Yourself
- Enable 2FA on all exchanges and wallets.
- Never share your seed phrase or private keys.
- Use cold wallets for storing large amounts of crypto.
- Verify URLs before logging in to wallets or exchanges.
- Ignore unsolicited messages offering investment tips or giveaways.
How Does Crypto Make You Money?
Cryptocurrency isn’t just about buying and holding coins like Bitcoin. It offers multiple ways to make money—some fast and risky, others slow and steady. Whether you’re a beginner or a more experienced investor, here’s how crypto can make you money in simple terms.
This is the most common way people earn with crypto. You buy a coin (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum) when the price is low, then sell it later when the price goes up. If you enjoy fast-paced action, you can buy and sell coins within hours or days to profit from short-term price movements.
If you hold coins like ETH, SOL, or ADA, you can “stake” them—this means locking your coins to help support the network. Some platforms (like Aave or Compound) let you lend your crypto to others, and you earn interest. It’s like being your own bank. The rates can be higher than banks, especially with stablecoins like USDT or USDC.
Some blockchain games reward players with crypto or NFTs for playing. This is called Play-to-Earn (P2E). Some crypto projects give away free coins (called airdrops) to attract users. Airdrops can be worth hundreds or thousands of dollars if the project succeeds.
FAQs
Q: What’s the easiest way to buy crypto?
A: Use a trusted exchange like Coinbase or Binance, set up KYC, link a bank, and buy.
Q: Which crypto is best for beginners?
A: Bitcoin and Ethereum—they’re the most popular and widely supported.
Q: How do I store crypto safely?
A: Use hardware (cold) wallets plus 2FA on exchanges.
Q: Can I lose money in crypto?
A: Yes—due to price swings, hacking, or scams. Only invest what you can afford to lose.
Q: Is crypto legal in my country?
A: Rules differ. Most nations allow it with some regulation, while a few ban certain uses.
Q: How to store cryptocurrency
A: Storing cryptocurrency safely is one of the most important steps after buying it. Unlike regular money in a bank, you are fully responsible for the safety of your crypto. If you lose access to your wallet or fall for a scam, there’s no customer service to recover your funds.
Q: Is Cryptocurrency a Safe Investment?
A: Cryptocurrency has gained massive attention in recent years, especially with coins like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH) reaching all-time highs and attracting both everyday users and large institutions. But it depends on your knowledge, risk tolerance, and how you manage your investments.
Q: Is Crypto Real Money?
A: One definition of money is something that is generally accepted as a medium of exchange, a measure or store of value, and a unit of account. By this definition, cryptocurrency is real money.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency is more than just digital money—it’s a new financial system. It offers freedom, simplicity, and innovation, but it comes with risk. As crypto grows—through DeFi, NFTs, and even government adoption—being informed and careful is key.
✅ Want to Learn More?
⚠️ Disclaimer
This article is for educational purposes only. It does not offer financial or investment advice. Crypto markets are volatile, and past trends don’t guarantee future results. Always do your own research and consider consulting a financial advisor before investing.