What is the Internet of Things?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical objects—”things”—embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet. These devices range from ordinary household items like lightbulbs, thermostats, and refrigerators to sophisticated industrial tools and healthcare equipment.
Unlike traditional internet-connected devices such as computers and smartphones, IoT devices operate with minimal human intervention. They collect, share, and act on data, creating a more seamless connection between the physical and digital worlds. At its core, IoT is about extending the power of internet connectivity beyond standard devices to a wide range of everyday objects, enabling them to communicate, collect data, and be remotely controlled or monitored.
How does IoT work?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is important because it enables smarter, more efficient, and data-driven operations across everyday life and industries. By connecting devices and systems, IoT provides real-time insights that improve decision-making, automation, and productivity. It helps businesses reduce costs through predictive maintenance, optimize resource usage, and enhance customer experiences. In areas such as healthcare, transportation, manufacturing, and smart cities, IoT improves safety, efficiency, and sustainability. Overall, IoT plays a crucial role in digital transformation by turning data into actionable intelligence and enabling more connected and responsive environments.
How Does the Internet of Things Work?
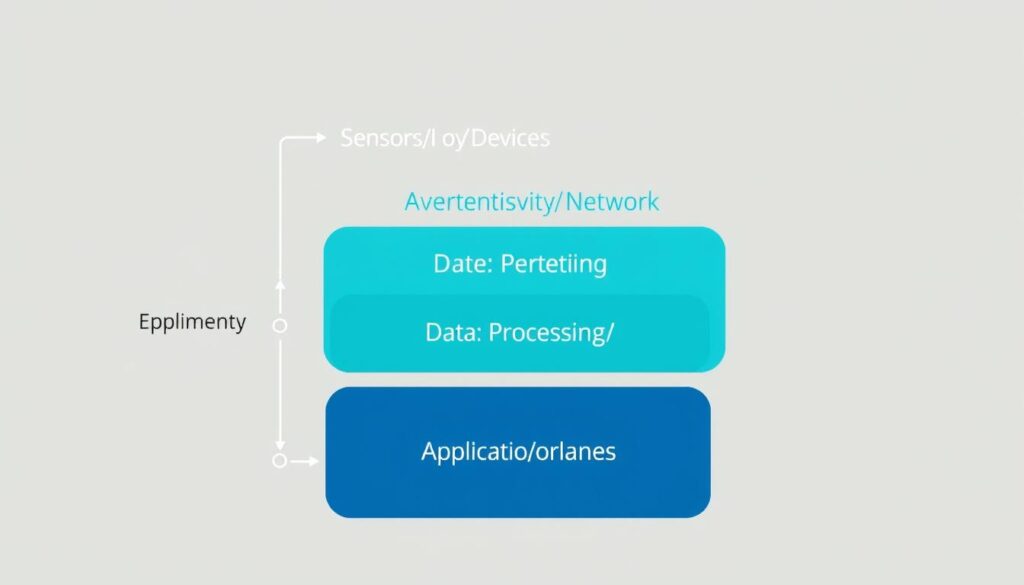
The Internet of Things functions through an ecosystem of components working together. Understanding these components helps clarify how this technology creates value:
IoT Components and Architecture
Sensors and Devices
IoT begins with devices equipped with sensors that collect data from their environment. These sensors can measure temperature, motion, moisture, light, sound, or almost any other physical parameter. For example, a smart thermostat uses temperature sensors to monitor your home.
Connectivity
The collected data is sent to a cloud infrastructure through various connection types, including cellular, satellite, WiFi, Bluetooth, or direct internet connection. The connectivity method depends on the specific IoT application and its requirements.
Data Processing
Once the data reaches the cloud, software processes it. This might involve checking that the temperature reading is within an acceptable range or analyzing patterns in motion sensor data to detect unusual activity.
User Interface
The information is made useful to end-users through an application or interface. This could be a mobile app that alerts you when your home’s temperature drops below a certain level or a dashboard showing industrial equipment performance.
Action
Based on the processed information, the system can automatically adjust settings, send alerts, or perform other actions. For instance, your smart thermostat might automatically adjust the temperature based on your preferences.
Artificial Intelligence
Many IoT systems incorporate AI and machine learning to improve over time. These systems analyze patterns in the collected data to make better predictions and decisions without human intervention.
Get Your Free IoT Beginner’s Guide
Want to learn more about how IoT can benefit your home or business? Our comprehensive guide explains everything in simple terms with practical examples you can implement today.
Real-World Internet of Things Examples
The Internet of Things has applications across virtually every industry and aspect of daily life. Here are some of the most common and impactful examples:
Consumer IoT Applications

Smart Home Devices
Smart home technology represents one of the most recognizable applications of IoT. These systems allow homeowners to control and automate various aspects of their living environment:
- Smart thermostats like Nest or Ecobee learn your preferences and adjust temperature automatically, saving energy and improving comfort
- Connected lighting systems that can be controlled remotely or programmed to respond to specific conditions
- Smart security systems with cameras, motion sensors, and automated alerts
- Voice assistants like Amazon Echo or Google Home that control other smart devices

Wearable Technology
Wearable IoT devices have become increasingly popular for health monitoring and convenience:
- Fitness trackers monitor physical activity, sleep patterns, and heart rate
- Smartwatches extend smartphone functionality to your wrist
- Medical wearables that monitor specific health conditions and alert caregivers when necessary
- Smart clothing with embedded sensors for athletic performance tracking
Industrial IoT Applications

Manufacturing and Industry
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is transforming manufacturing and industrial processes:
- Predictive maintenance systems that identify potential equipment failures before they occur
- Production line monitoring that improves efficiency and reduces downtime
- Inventory management systems that automatically track supplies and order replacements
- Quality control processes enhanced by sensor data and real-time analytics
Smart Cities
Cities worldwide are implementing IoT solutions to improve infrastructure, services, and quality of life:
- Smart traffic management systems that reduce congestion and improve flow
- Connected public transportation that provides real-time updates and optimizes routes
- Smart utility meters that monitor water and electricity usage
- Environmental monitoring for air quality, noise levels, and other factors
- Smart waste management systems that optimize collection routes

Healthcare IoT
IoT is revolutionizing healthcare delivery and patient monitoring:
- Remote patient monitoring devices that track vital signs and medication adherence
- Smart hospital rooms that adjust lighting, temperature, and entertainment based on patient preferences
- Connected medical equipment that ensures proper utilization and maintenance
- Real-time location systems that track medical equipment, staff, and patients
Agriculture
Smart farming uses IoT to optimize agricultural processes:
- Soil moisture sensors that enable precise irrigation
- Weather stations that provide localized forecasts for crop management
- Livestock monitoring systems that track animal health and location
- Automated greenhouse systems that maintain optimal growing conditions
Benefits of the Internet of Things
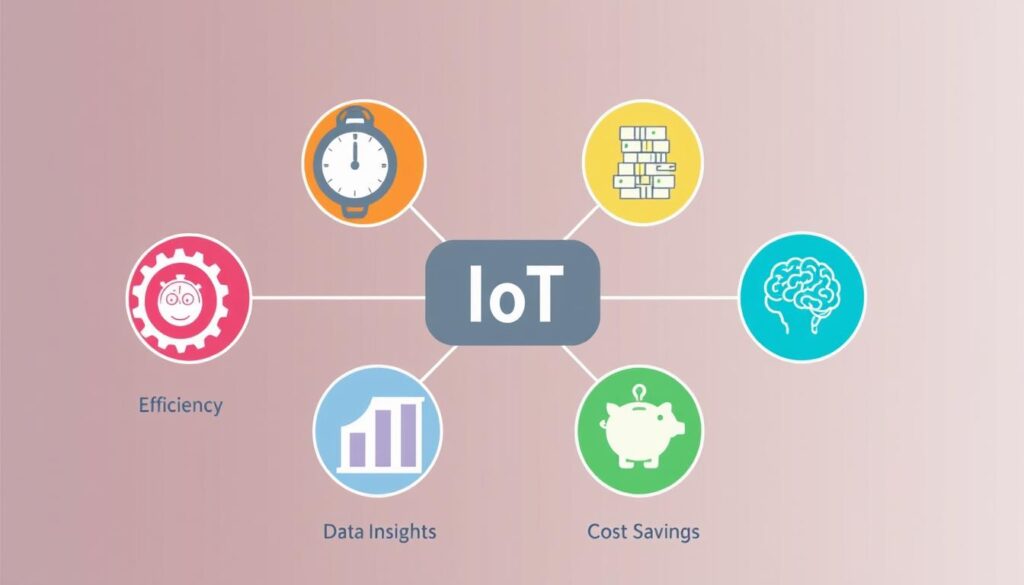
The Internet of Things (IoT) offers numerous benefits by enabling devices to connect, communicate, and share data in real time. IoT improves operational efficiency through automation, reducing manual tasks and human error. It enhances decision-making by providing accurate, real-time insights from connected sensors and devices. Businesses benefit from predictive maintenance, which helps prevent equipment failures and reduce downtime. IoT also improves user convenience and experiences through smart homes, connected healthcare devices, and intelligent transportation systems. Overall, IoT drives cost savings, productivity, and innovation across industries.
Challenges and Concerns with IoT
Security and Privacy Concerns

The proliferation of connected devices creates new security vulnerabilities:
- Many IoT devices lack robust security features, making them vulnerable to hacking
- Connected systems create multiple entry points for cyberattacks
- Personal data collected by IoT devices raises significant privacy concerns
- Security patches and updates can be difficult to implement across large IoT deployments
Risks and challenges in IoT

The future of the Internet of Things (IoT) is set to be shaped by advancements in connectivity, intelligence, and scalability. Technologies such as 5G and edge computing will enable faster data processing and lower latency, supporting real-time IoT applications. Artificial intelligence and machine learning will increasingly be integrated into IoT systems to provide smarter automation, predictive analytics, and autonomous decision-making. Security and privacy will also become top priorities, driving the adoption of stronger encryption, device authentication, and regulatory compliance standards. Additionally, the growth of smart cities, connected healthcare, and industrial IoT will continue to expand IoT’s role across industries, making it a core component of future digital infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions About IoT
What do you mean by Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity. These devices collect and exchange data over the internet, enabling smarter automation, monitoring, and decision-making.
What is IoT and examples?
IoT is the connection of everyday devices to the internet to share data and interact intelligently. Examples include smart home devices like thermostats and lights, wearable fitness trackers, connected cars, industrial sensors, and smart city applications such as traffic monitoring systems.
What are the 4 types of IoT?
The four main types of IoT are:
- Consumer IoT (CIoT): Devices used by individuals, like smart speakers and wearables.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): Machines and sensors used in manufacturing and supply chains.
- Infrastructure IoT: Devices that monitor and manage urban or environmental infrastructure, like smart grids and traffic systems.
- Enterprise IoT: IoT applications within organizations for business operations, logistics, and asset management.
What is an IoT network used for?
An IoT network is used to connect IoT devices so they can communicate, share data, and operate collaboratively. These networks support automation, real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and intelligent decision-making across industries, homes, and cities.
What’s the difference between IoT and M2M?
Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communication refers to direct communication between devices using any communications channel. IoT is broader, typically involving internet connectivity, cloud computing, and more complex networks of devices. IoT can be thought of as an evolution of M2M technology with enhanced capabilities.
How secure is the Internet of Things?
Security varies widely across IoT implementations. Many consumer IoT devices have been criticized for inadequate security measures. Enterprise and industrial IoT solutions typically implement stronger security protocols. As the technology matures, security standards are improving, but it remains a significant concern that requires ongoing attention.
How much data do IoT devices generate?
The amount varies dramatically by device type and application. A simple temperature sensor might generate only a few kilobytes daily, while a connected car can produce up to 25GB per hour. Collectively, IoT devices are expected to generate over 79 zettabytes of data by 2025 (a zettabyte is one trillion gigabytes).
Do all IoT devices need internet connectivity?
Not necessarily. Some IoT devices communicate through local networks without direct internet access. However, to realize the full benefits of IoT—such as remote monitoring, control, and data analysis—internet connectivity is typically required, either directly or through a gateway device.
Ready to Implement IoT in Your Environment?
Whether you’re looking to create a smarter home or implement IoT solutions in your business, our implementation checklist will help you get started with confidence. Download it now to avoid common pitfalls and maximize your IoT investment.
Conclusion

The Internet of Things represents one of the most significant technological shifts of our time. By connecting the physical and digital worlds, IoT is creating unprecedented opportunities for improving efficiency, enhancing experiences, and solving complex problems across virtually every industry and aspect of daily life.
While challenges remain—particularly around security, privacy, and interoperability—the trajectory is clear. As 5G networks expand, edge computing matures, and AI capabilities advance, IoT will become increasingly powerful, pervasive, and essential to modern life and business operations.
Whether you’re a consumer looking to make your home smarter, a business leader seeking operational efficiencies, or simply curious about this transformative technology, understanding the Internet of Things is an important step in navigating our increasingly connected future.